AQUACULTURE
Fish culture classification:
- Extensive: least managed fish farming.
- Intensive: Best managed fish farming. Maximum production with minimum qty of water & fed on artificial food, pond management by use of fertilizers. High production (6000kg/ha/year) with high quality fish.
- Semi intensive: Between the first two kinds.
Pond: Best pond depend upon quantity, Depth & quality of water.
Quantity of water depend upon rate of evaporation of water. Evaporation of water in temperate climate at the rate of 1litter per hectare per second to 2.5 cm per day.
Depth of 1 to 1.5 meter is generally suitable .However too deep water poses problem of drainage as well as differential temp. in different depth level which is harmful to production.
Water Quality of pond water is judged by its Biogenic capacity. Its capacity to produce the natural food to feed and sustain fish. Water is said to be poor, average or rich depending upon its biogenic capacity.
The quality of water depending upon physico chemical parameters like Temperature, turbidity, Dissolved oxygen, PH, Alkalinity.
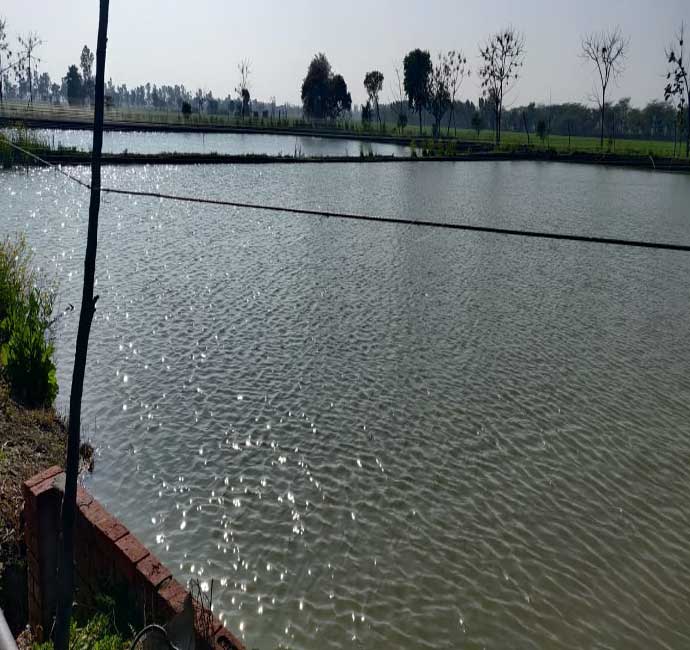


Ideal pond should have Green & Brown colour( due to presence pf plankton) PH level between 7.8 to 8.5, Alkalinity in Range of 150 to 200 ppm, Turbidity at 200 ppm,& Dissolve Oxygen at 4 to 6 ppm (6-7 mg/litre).
Temperature: Fish have different ranges of temperature tolerance. Growth, Reproduction & breathing rate directly depend upon temperature variation.
Temperature between 20 -37 is suitable for major carps. Below 16 & above 40 temperature indian major carps cannot survive.
Turbidity: In general turbidity affects penetration of sun light and therefor is unfavourable to photosynthetic activity in pond water which effect on DO of water.
Dissolve Oxygen: when water is having lowered concentration of oxygen, fish begin to rise to surface or crowed near the inlet. In extreme depletion of DO level fish may die of Asphyxia.
Variation in Concentration of DO may occur due to several parameters
- Cloudy days reduce it
- Higher temperature decrease it
- Higher salinity lower it
- Decomposing organic matter,Sewage fertilizers, manures lowered DO.
Due to photosynthesis DO in Day time is high but it goes down considerable. In some cases it lead to dangerous fall in the level during night in pond with excessive abundance of algae and submerged weeds or even during day in cloudy day.
PH Level: Cultivable fishes tolerate different range of PH. But sudden Fluctuations in PH is harmful. In general PH7-8 water is more productive than acidic water. PH below 4.5or above 9 is particularly injurious & unproductive. Acid water has following adverse effect.
- It reduces growth rate by Decreasing the appetite of fish.
- It increasing chances of microbial infection, occurrence of diseases & attack of parasites.
- It has toxic effect.
- It lowered dissolve carbon dioxide content , reducing photosynthetic activity.
- It remove lime from water thereby affecting growth of skeletal tissues & scales.
Fish Production: Three kind of production are distinguished.
- Quantitative Production: Is characterized by as great a quantity of fish as possible, with no regard to grade and quality of fish.
- Qualitative production: Has the main aim of producing fish of high quality that is uniform size, weight & high commercial value.
- Economic Production: Amis at producing as high a quantity of fish of great market value as possible. Here both the totalweight of the fish harvested as well as the weight of individual fish are important.

Pond management, Improvement and Restoration:
Control of unwanted vegetation (weeds): It harm in several ways the pond productivity
- It provides shelter for food competitors for fish.
- It increases sliting, restricting fish movement.
- It shades water ,cutting the sunlight penetration.
- It turns the pond into swamp (daldal).
The elimination of the excess weed is necessary to improve fish production of pond.
- Drying out of the pond: The pond become hygienic by destruction of the disease organisms , Intermediate host of fish parasites & by destruction of fish enemies including insects and their larvae.
- Increasing pond Depth: By removing deposition mud at the bottom helps destroys the roots of emergent vegetation (weeds) and also bringing the deep sterile layers of soil.
- Dredging: Is necessary to restore its productivity.
-
Liming the pond:
# Lime is antiparasitic, destroying parasites living in the water.
# It destroys the algae & submerged weeds.
# It kills the fish enemies such as insects and their larvae.
# It correct the acid water to make it slightly alkaline (PH 7-8).
- Fertilizers: Use of fertilizer( organic fertilizer like compost,cowdung) to increase fish production in the pond. It increases the natural food in the pond also improve hygienic condition of pond by speeding up the decomposition of food residues.( inorganic fertilizer like lime, phosphate, potash, nitrogenous compound and magnesium fertilizer)
On the basis of the production of the nutritive fauna pond are classified as
- Oligotrophic: water poor in minerals and appearing clear & blue when deep.
- Eutropic: Rich in minerals & plankton. Appearing green or brown-green.
- Destrophic: Water rich in colloidal humus and peat appearing yellow orbrown.
Fish Pathology, Aetiology & Therapy of Diseases
Commonest factor favouring outbreak of diseases is Density of fish culture practices. Fish in Tropical water are more susceptible to diseases than fishes in temperature water because such water get easily polluted from unused food and decomposing organic matter and lead to unhygienic condition, Oxygen Depletion, Fluctuation in Temperature, Alteration in PH ranges. All these contribute to create of condition favourable to quick spread of diseases. In this condition fish become SICK. Sick fish sooner or later get easily infested with parasites because resistance is lowered in the body.
Sign of Sickness of Fish:
- Fish becomes listless
- Loss of balance unable to maintain its position in the column of water.
- Fish tends to lie on its side either resting at the bottom or floating at the surface.
- Tail & fin do not seem to function normally & with vigour.
- Persisting discolouration is common on body.
- Gills appear pale.
- Slimy, Grey excretions on skin.
Simple test for sick fish: Hold the fish in the hand under water and turn it on to its one side. If the eye ball also turns following the turning of the body, the fish is very sick.
Sick fish is less timid or agile in its reaction to external disturbance or not at all. When taken out of water fish is not violent and may be calm and sluggish from the very beginning.
When hold in hand by head and trunk and tail allowed freedom, a sick fish lets this part of the body hang down vertically with fin folded and not let remain horizontal with fin spread out.

Procedures for Diagnosis of Fish disease:
- Assessment of fish Environment: Examination of health condition of fish water. Such as smell, transparency, colour, oxygen content, temperature, pollutant etc.
- Assessment of health of fish: Common test include those on escape reflex, Defensive reflex, Tail reflex, Ocular reflex.
- Assessment of possible causes of sickness: carps and other fish species come to surface show little escape reflex, after some time sink to bottom and lie there waiting death.
Carps come to surface and gulp air bubbles at the surface very frequently, after some time fish start dying with mouth open wide and opercula spread apart.
Gill damage due to parasitic disease.
Nutritional Diseases:
- Arising from undernutrition
- Arising from dietary deficiency or imbalances in major components of food.
- Arising from toxic effect of the diet.
Diseases due to mal nutrition is
Pin heads: Enlarged head with slender body, are starved larvae in nurseries or starvation may arise from inadequate supply of food or starvation in overstocking condition.
Lipoid hepatic Degeneration: liver turns yellow brown colouration. Anaemia follows with Gills looking pallor.
Vitamin A, B6,& Vitamin C deficiency also detected.
Diseases due to environmental factor:
- Alteration of water PH. If the water PH too acidic (below5.5) or too Alkaline(above9). The skin of fish gets covered with whitish film and gills turn brownish at the edge. Mucus secretion is enhanced. In latter case the gills appear burnt and fins givean Injured look.
- Due to asphyxia fish show sign of suffocation, mouth wide open, gill opercula raised and gills spread wide apart.
- Due to chill & cold following drop in temperature of water. The symptoms include congestion of gill apparatus and dull appearance of fish.
- Due to constipation and indigestion fish show symptoms include queer movements and listlessness. Stomach appears swollen and scales erected.
- Egg binding illness of females. The body of the females greatly swollen due to accumulation of ripe eggs that could not be released.
Diseases caused by parasites and pathogens:
Bacterial Diseases: Abdominal dropsy of carps is very common during spring in temperature climate symptoms include general oedema, accumulation of watery liquid, yellow or pink in colour, in the body cavity and withering away of fins.
Furunculosis also bacterial disease with characteristic symptom is the appearance of furuncles(boils). These are rounded swellings appearing on the side of the body. Each swelling contains a pus like substance. The swelling often bursts releasing the content into the water.
- Viral Diseases: the symptoms include general anaemia, pale discolouration of gills, swelling of eyes and belly, oedema of muscles, Inflammation of intestines. Sores may appear on skin, anus may be protruded.
- Protozoan diseases: The main symptoms is the appearance of a slimy secretion on the skin, fins & on the gills. The affected surface looks covered with a light grey fog. In very advance stages red patches may also appear of affected parts. Fins may be folded up and gills partially destroyed.
- Fungal Diseases: This disease characterized by appearance of tufts of cotton wool on the skin. Appearance of small white tufts on fins and skin.
- Common Ectoparasites:Fish lice infection is one of the commonest infection. It sucking the blood under layers of the surface Fish leech infection.